Canalys is part of Informa PLC
This site is operated by a business or businesses owned by Informa PLC and all copyright resides with them. Informa PLC’s registered office is 5 Howick Place, London SW1P 1WG. Registered in England and Wales. Number 8860726.

Smart rings: a new frontier for device vendors?
With Samsung becoming the first major vendor to develop a smart ring, we look at some of the key reasons behind this move and offer recommendations to mitigate the risks associated with smart ring development.

Canalys defines a smart ring as a finger-worn device that features tracking sensors. It may or may not have a display and is connected via a smartphone. Its primary function is health and fitness tracking, but it can also have additional features, such as NFC or the ability to act as a control hub for ecosystem devices.
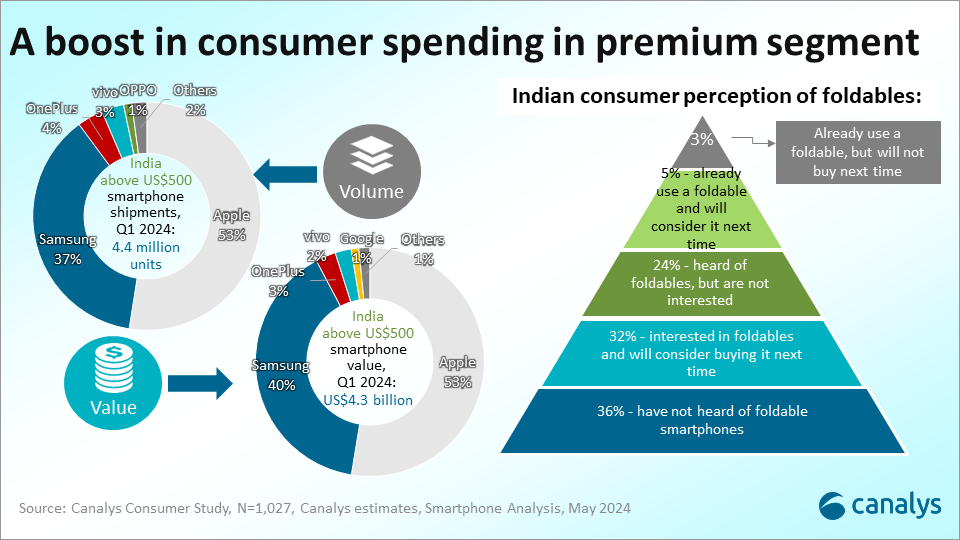
Samsung is the first major ecosystem vendor to enter the smart ring market with its new Galaxy Ring. Samsung’s entry will increase the visibility of smart rings and attract a wider audience of fashion and fitness enthusiasts.
But Samsung’s entry will also attract competition. As a vendor that operates in fiercely competitive device categories, Samsung will aim to take the first-mover advantage with its smart ring to help diversify its portfolio, differentiate and find new revenue streams. But with other vendors expected to enter the smart ring market soon, the more important question is:
Why are vendors investing in smart rings?
1. To appeal to non-watch users and expand their user bases
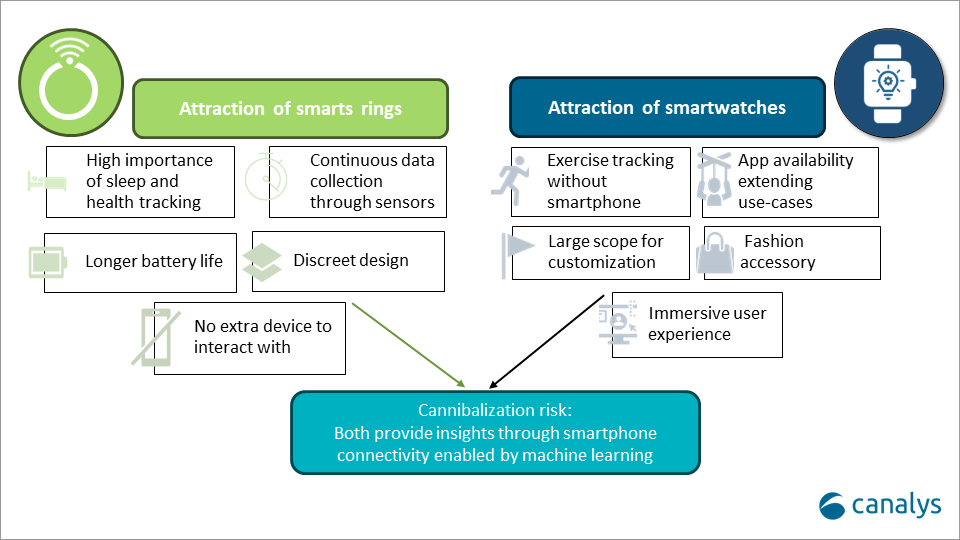
With growth rates in the wearable band market flattening, the novel form factor presents a key opportunity to attract customers. The discreet, minimalist and stylish design adds an allure that can help vendors reposition their brands as fashionable. Smart rings can reach customers that haven’t been attracted by smartwatches.
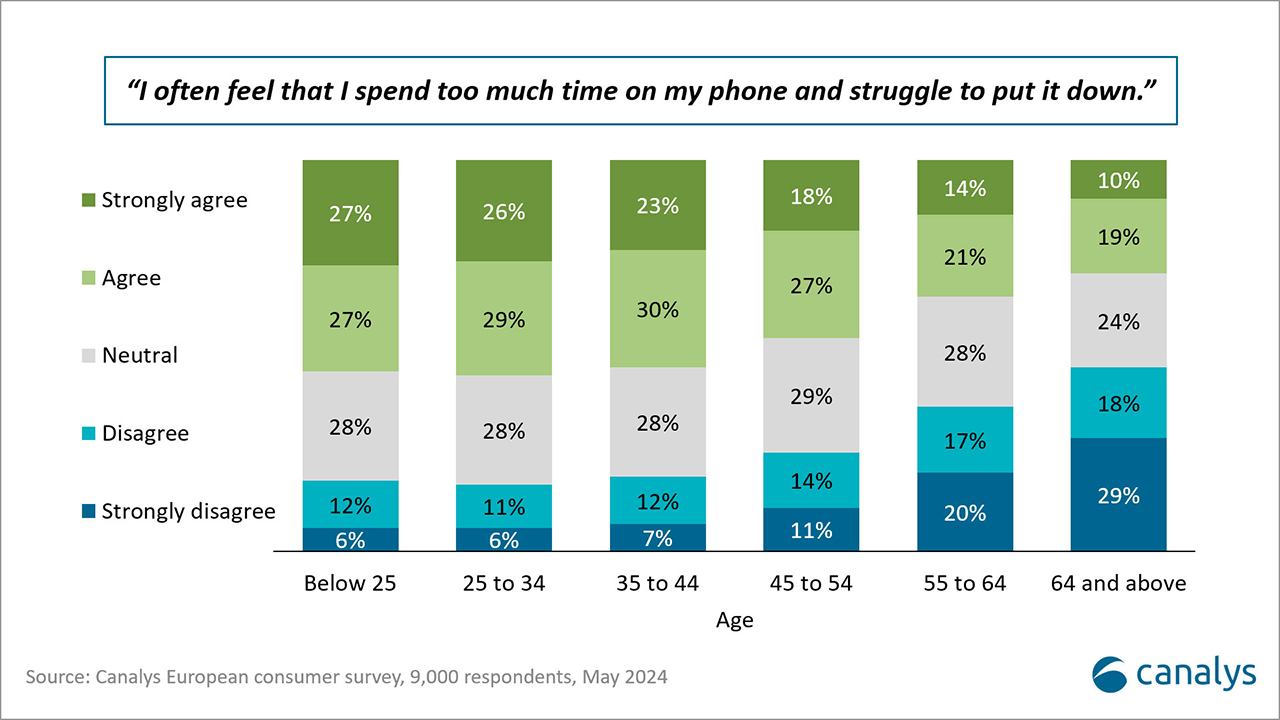
Furthermore, smart rings can provide a substitute for wearable bands for users seeking to reduce screen time. In a Canalys study from May 2024 of 9,000 consumers in Europe, almost 50% of respondents stated that they feel that they spend too much time on screens and struggle to reduce their screen time. This trend is particularly strong among younger respondents, with growing concerns around eye health and wellbeing. Though smart rings will not provide a comprehensive solution, they can help alleviate concerns by reducing screen exposure while still tracking essential metrics.
2. To target wellness-focused customers
Health and fitness tracking are the core use cases for wearable bands. Smart rings excel in sleep tracking and can add to the complete tracking experience for health and fitness-focused users. Sleep tracking is the fastest-growing interest area among consumers. Smart rings tend to offer greater accuracy than wrist-based counterparts and do not need to be charged as often as smartwatches.
3. For more accurate tracking to support the ecosystem experience
Smart rings have the potential to offer more accurate tracking than wearable bands due to their proximity to large blood vessels, enhancing the overall user experience. Seamless integration between a ring, watch and phone provides a comprehensive health and fitness tracking experience, maximizing user satisfaction. Strong integration not only improves upselling opportunities but also strengthens customer loyalty for future purchases. This can be achieved without significant cannibalization of wearable band shipments, as the differing use cases allow rings and watches to be used together effectively.
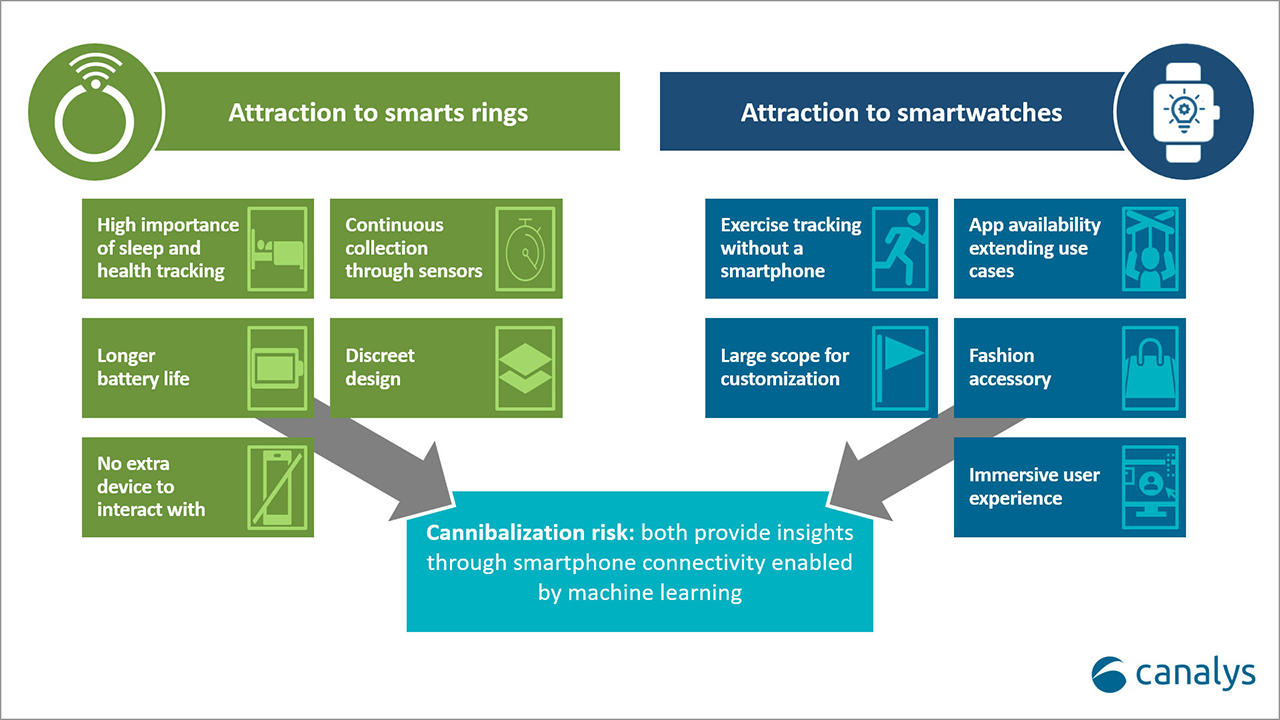
4. To redefine the user experience
Furthermore, there is potential for smart rings to become gesture control hubs for ecosystem devices, such as PCs or even AR/VR devices.
Gesture controls are the growing trend in wearable bands, reducing the dependence on direct screen interaction. The adoption of gesture controls is currently led by Apple, but other vendors will likely follow.
While gesture controls are a handy feature for wearable bands, the touchscreen remains the control hub. But on smart rings, gesture controls can enhance device functionality and provide a further leap for the user experience. Gesture controls can counter the perceived lack of control options directly on the device, though this will require sufficient user education.
5. To elevate brand positioning and innovation leadership
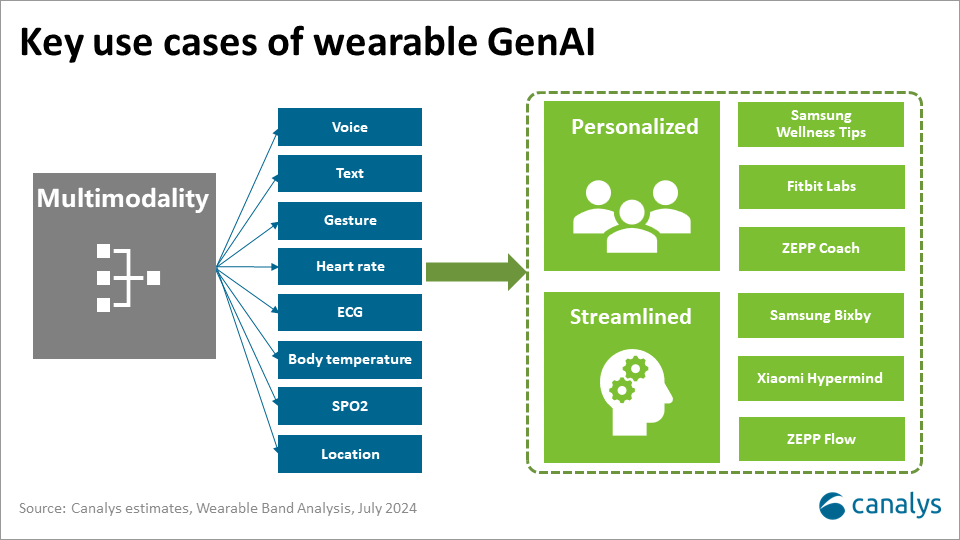
Integration of generative AI promises enhanced analytics that can be better enabled by smart ring tracking. For example, sleep tracking forms the basis of new consumer insights, such as energy and rest scores. By leading with AI capabilities across the ecosystem and innovative form factors, vendors can position and differentiate their brands as market-leading and forward-thinking.
Furthermore, the compact size of smart rings will push vendors to innovate and improve smaller components. These advances can subsequently be extended to wearable bands and help innovation for the wider category, enabling slimmer designs and increasing battery life.
6. To diversify portfolios in search of new revenue streams
Identifying new monetization opportunities and revenue streams is high up on vendors’ priority lists in 2024. Diversifying portfolios can allow companies to attract new consumers, create new use cases and build new services, and has the long-term potential to expand revenue streams.
Risks and recommendations
Smart rings provide many opportunities for vendors, but it is still early days. Some of the risks vendors need to be aware of include:
- Innovation can slow down due to challenges with the rings’ tiny size and lack priority due to the small initial market size. Innovation in cloud-based AI-driven insights will be vital to elevate products over time, alongside multi-modal controls, such as voice inputs and gestures. This could potentially limit the market’s growth potential.
- Current price points will damage the appeal for a large proportion of the audience, as shown by worryingly low pre-sales for many devices. But strong innovation and price competition will help to correct this.
- Due to the limited scope for differentiation within rings, a homogenous product market may result in the strongest brands taking the largest shares, outcompeting smaller and medium-sized vendors.